Schedule
The events are scheduled in Beijing time (UTC+8 / GMT+8). You can find the schedule in PDF format here.
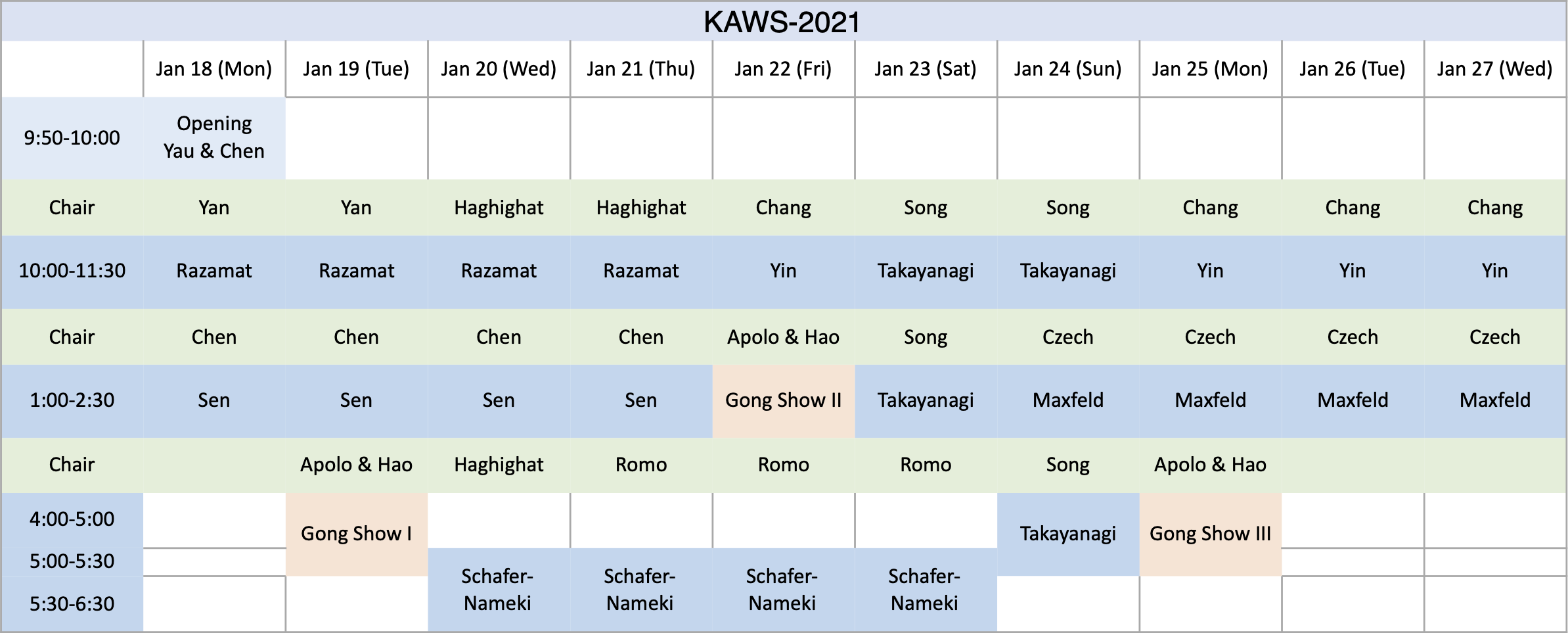
Lectures
Henry Maxfield: Black hole information and spacetime wormholes
Shlomo Razamat: Aspects of supersymmetric dynamics and geometry
Lecture I
Basic techniques: Overview of supersymmetric QFTs in D ≤ 6. Lagrangians and RG flows in and between dimensions. Basics of supersymmetric dynamics in D = 4. Basic computational techniques: anomalies, a-maximization, superconformal index, conformal manifolds.
References:
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.08946.pdf (in particular sections 3,7,8)
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/hep-th/0304128.pdf; https://arxiv.org/pdf/1005.3546.pdf
Lecture II
IR dualities. Emergence of symmetry in the IR and conformal dualities: two case studies of emergence of symmetry and a conformal duality. General algorithm of deriving conformal dual Lagrangians for a given SCFT. Interplay between dualities and IR emergence of symmetry.
References:
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.08946.pdf (Section 4)
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.02789.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1906.05088.pdf
Lecture III
Geometrization of 4d dynamics: analysis of compactifications of the minimal SU(3) SCFT in 6d to 4d.
References:
Lecture IV
Dualities and group theory: compactifications of the E-string theory to 4d. Geometrization and generalization of Seiberg dualities.
References:
Sakura Schafer-Nameki: Geometry and 5d SCFTs
The main topic of these lectures are 5d superconformal field theories (SCFTs). I will discuss their Coulomb and Higgs branches description, the realization in M-theory on Calabi-Yau threefolds, and their relation to 6d SCFTs.
Ashoke Sen: How to compute string amplitudes?
The usual approach to computing string amplitudes uses world-sheet techniques, expressing the amplitudes as integrals over the moduli spaces of Riemann surfaces. However these integrals often run into divergences from the boundaries of the moduli spaces. We shall discuss various situations where such divergences appear and show how we can use insights from string field theory to remove these divergences. The discussion will focus on, but will not be limited to, D-instanton contribution to string theory amplitudes.
Tadashi Takayanagi: Quantum Entanglement and Holography
In this lecture, we will explain recent developments of quantum information aspects of holography (or AdS/CFT correspondence). Starting from the basic aspects of quantum entanglement, we will explain calculations of entanglement entropy in conformal field theories (CFTs) and in the AdS/CFT. After we introduce the modern understanding of
structure of holographic duality, namely entanglement wedges, we will end up with gravity duals of conformal field theories on manifolds with boundaries (called boundary conformal field theories, BCFTs), which have been applied to black hole information problems recently.
We will cover the following topics
- (1) Basics of Quantum Entanglement
- (2) Entanglement Entropy in CFTs
- (3) Holographic Entanglement Entropy
- (4) Entanglement Wedges and Bulk Reconstruction
- (5) Holography for BCFTs and Recent Applications to Black Hole Information
References:
- (1): M.A. Nielsen, I. L. Chuang, “Quantum Computation and Quantum Information”, Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-63503-5.
- (2,3,4): M. Rangamani and T.Takayanagi, ``Holographic Entanglement Entropy'', Lect. Notes Phys. 931 (2017), pp.1-246, [arXiv:1609.01287 [hep-th]].
- (5): M. Fujita, T. Takayanagi and E. Tonni, ``Aspects of AdS/BCFT'', JHEP 11 (2011), 043 [arXiv:1108.5152 [hep-th]] + recent papers
Xi Yin: 2D string theory
c=1 string theory, also known as the 2D bosonic string theory, is the only known version of bosonic string theory that admits a worldsheet CFT description and a space-time interpretation. We will introduce the worldsheet theory based on Liouville CFT, discuss the computation and interpretation of closed string amplitudes, as well as the matrix model dual and the fermi sea/collective field description of the latter. I will discuss the role of ZZ-instantons and the non-perturbative completion of the dual matrix model. Finally, I will discuss the role of FZZT branes, long strings and the non-singlet sector of the matrix model, and c=1 string theory in the 2D black hole background. I will comment on the 2D type 0 string theory if time permits.
References:
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.07151.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.07233.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.07688.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1912.07170.pdf